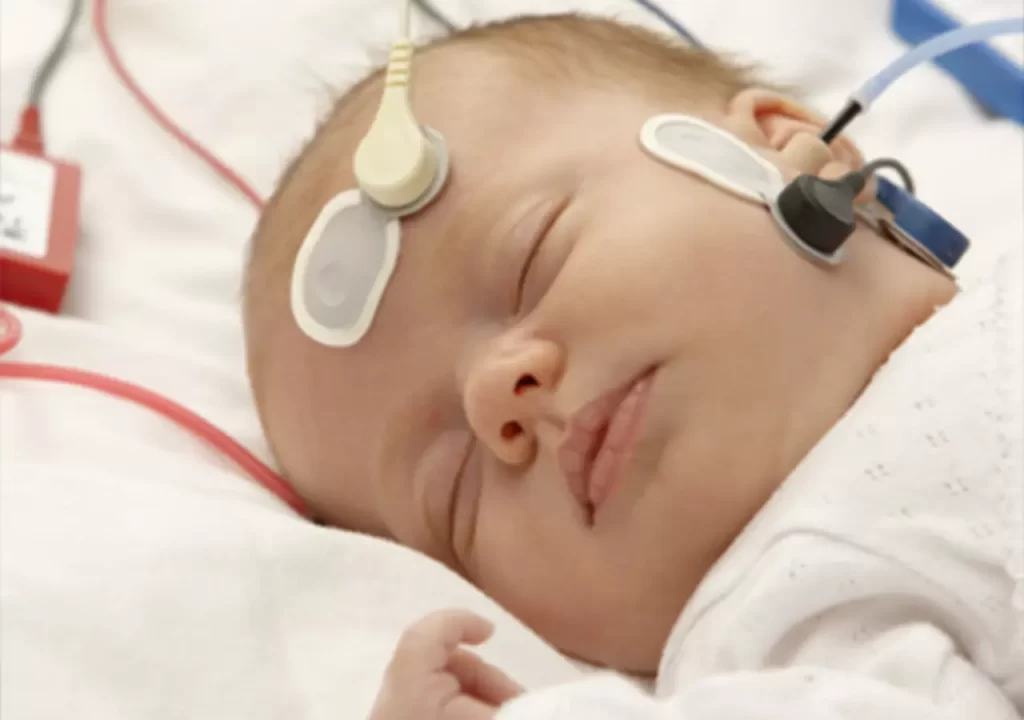
Auditory steady state response is a type of evaluation that is commonly used for children who are too young to actively participate in more traditional auditory hearing tests. During this procedure, electrodes are used to record the individual’s brain activity in response to a variety of sounds. These recordings are then analyzed using computer software to determine the lowest frequency that a person is capable of hearing. An ASSR typically uses frequency specific stimuli (0.5, 1, 2, 4 kHz) with the goal of creating an estimated audiogram. In other words, it is a test used for performing a threshold assessment.